Data sorting and pipes dplyr
Overview
Teaching: 60 min
Exercises: 7 minQuestions
How can I sort the rows in my data?
How can I avoid storing intermediate data objects?
Objectives
Use
arrange()to sort rowsUse the pipe
%>%to chain commands together
Motivation
Getting an overview of our data can be challenging. Breaking it up in smaller pieces can help us get a better understanding of its content. Being able to subset data is one part of that, another is to be able to re-arrange rows to get a clearer idea of their content.
Creating subsetted objects
So far, we have kept working on the penguins data set, without actually altering it. So far, all our actions have been executed, then forgotten by R. Like it never happened. This is actually quite smart, since it makes it harder to do mistakes you can have difficulties changing.
To store the changes, we have to “assign” the data to a new object in the R environment. Like the penguins data set, which already is an object in our environment we have called “penguins”.
We will now store a filtered version including only the chinstrap penguins, in an object we call chinstraps.
chinstraps <- filter(penguins, species == "Chinstrap")
You will likely notice that when we execute this command, nothing is output to the console. That is expected. When we assign the output of a function somewhere, and everything works (i.e., no errors or warnings), nothing happens in the console.
But you should be able to see the new chinstraps object in your environment, and when we type chinstraps in the R console, it prints our chinstraps data.
chinstraps
# A tibble: 68 × 8
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 Chinstrap Dream 46.5 17.9 192 3500
2 Chinstrap Dream 50 19.5 196 3900
3 Chinstrap Dream 51.3 19.2 193 3650
4 Chinstrap Dream 45.4 18.7 188 3525
5 Chinstrap Dream 52.7 19.8 197 3725
6 Chinstrap Dream 45.2 17.8 198 3950
7 Chinstrap Dream 46.1 18.2 178 3250
8 Chinstrap Dream 51.3 18.2 197 3750
9 Chinstrap Dream 46 18.9 195 4150
10 Chinstrap Dream 51.3 19.9 198 3700
# … with 58 more rows, and 2 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>
Maybe in this chinstrap data we are also not interested in the bill measurements, so we want to remove them.
chinstraps <- select(chinstraps, -starts_with("bill"))
chinstraps
# A tibble: 68 × 6
species island flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex year
<fct> <fct> <int> <int> <fct> <int>
1 Chinstrap Dream 192 3500 female 2007
2 Chinstrap Dream 196 3900 male 2007
3 Chinstrap Dream 193 3650 male 2007
4 Chinstrap Dream 188 3525 female 2007
5 Chinstrap Dream 197 3725 male 2007
6 Chinstrap Dream 198 3950 female 2007
7 Chinstrap Dream 178 3250 female 2007
8 Chinstrap Dream 197 3750 male 2007
9 Chinstrap Dream 195 4150 female 2007
10 Chinstrap Dream 198 3700 male 2007
# … with 58 more rows
Now our data has two less columns, and many fewer rows. A simpler data set for us to work with. But assigning the chinstrap data twice like this is a lot of typing, and there is a simpler way, using something we call the “pipe”.
Challenge 1
Create a new data set called “biscoe”, where you only have data from “Biscoe” island, and where you only have the first 4 columns of data.
Solution 1
biscoe <- filter(penguins, island == "Biscoe") biscoe <- select(biscoe, 1:4)
The pipe %>%
We often want to string together series of functions. This is achieved using pipe operator %>%. This takes the value on the left, and passes it as the first argument to the function call on the right.
%>% is not limited to {dplyr} functions. It’s an alternative way of writing any R code:
The shortcut to insert the pipe operator is Ctrl+Shift+M for Windows/Linux, and Cmd+Shift+M for Mac.
In the chinstraps example, we had the following code to filter the rows and then select our columns.
chinstraps <- filter(penguins, species == "Chinstrap")
chinstraps <- select(chinstraps, -starts_with("bill"))
Here we first create the chinstraps data from the filtered penguins data set. Then use that chinstraps data to reduce the columns and write it again back to the same chinstraps object. It’s a little messy. With the pipe, we can make it more streamlined.
chinstraps <- penguins %>%
filter(species == "Chinstrap") %>%
select(-starts_with("bill"))
The end result is the same, but there is less typing and we can “read” the pipeline of data subsetting more like language, if we know how. You can read the pipe operator as “and then”.
So if we translate the code above to human language we could read it as:
take the penguins data set, and then keep only rows for the chinstrap penguins, and then remove the columns starting with bill and assign the end result to chinstraps.
Learning to read pipes is a great skill, R is not the only programming language that can do this (though the operator is different between languages, the functionality exists in many).
We can do the entire pipe chain step by step to see what is happening.
penguins
# A tibble: 344 × 8
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 181 3750
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 186 3800
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 195 3250
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA NA
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 193 3450
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 190 3650
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 181 3625
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 195 4675
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 193 3475
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 190 4250
# … with 334 more rows, and 2 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>
penguins %>%
filter(species == "Chinstrap")
# A tibble: 68 × 8
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 Chinstrap Dream 46.5 17.9 192 3500
2 Chinstrap Dream 50 19.5 196 3900
3 Chinstrap Dream 51.3 19.2 193 3650
4 Chinstrap Dream 45.4 18.7 188 3525
5 Chinstrap Dream 52.7 19.8 197 3725
6 Chinstrap Dream 45.2 17.8 198 3950
7 Chinstrap Dream 46.1 18.2 178 3250
8 Chinstrap Dream 51.3 18.2 197 3750
9 Chinstrap Dream 46 18.9 195 4150
10 Chinstrap Dream 51.3 19.9 198 3700
# … with 58 more rows, and 2 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>
penguins %>%
filter(species == "Chinstrap") %>%
select(-starts_with("bill"))
# A tibble: 68 × 6
species island flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex year
<fct> <fct> <int> <int> <fct> <int>
1 Chinstrap Dream 192 3500 female 2007
2 Chinstrap Dream 196 3900 male 2007
3 Chinstrap Dream 193 3650 male 2007
4 Chinstrap Dream 188 3525 female 2007
5 Chinstrap Dream 197 3725 male 2007
6 Chinstrap Dream 198 3950 female 2007
7 Chinstrap Dream 178 3250 female 2007
8 Chinstrap Dream 197 3750 male 2007
9 Chinstrap Dream 195 4150 female 2007
10 Chinstrap Dream 198 3700 male 2007
# … with 58 more rows
So, for each chain step, the output of the previous step is fed into the next step, and that way the commands build on each other until a final end result is made.
And as before, we still are seeing the output of the command chain in the console, meaning we are not storing it. Let us do that, again using the assignment.
chinstraps <- penguins %>%
filter(species == "Chinstrap") %>%
select(-starts_with("bill"))
chinstraps
# A tibble: 68 × 6
species island flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex year
<fct> <fct> <int> <int> <fct> <int>
1 Chinstrap Dream 192 3500 female 2007
2 Chinstrap Dream 196 3900 male 2007
3 Chinstrap Dream 193 3650 male 2007
4 Chinstrap Dream 188 3525 female 2007
5 Chinstrap Dream 197 3725 male 2007
6 Chinstrap Dream 198 3950 female 2007
7 Chinstrap Dream 178 3250 female 2007
8 Chinstrap Dream 197 3750 male 2007
9 Chinstrap Dream 195 4150 female 2007
10 Chinstrap Dream 198 3700 male 2007
# … with 58 more rows
Challenge 2
Create a new data set called “biscoe”, where you only have data from “Biscoe” island, and where you only have the first 4 columns of data. This time use the pipe.
Solution 2
penguins %>% filter(island == "Biscoe") %>% select(1:4)# A tibble: 168 × 4 species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> 1 Adelie Biscoe 37.8 18.3 2 Adelie Biscoe 37.7 18.7 3 Adelie Biscoe 35.9 19.2 4 Adelie Biscoe 38.2 18.1 5 Adelie Biscoe 38.8 17.2 6 Adelie Biscoe 35.3 18.9 7 Adelie Biscoe 40.6 18.6 8 Adelie Biscoe 40.5 17.9 9 Adelie Biscoe 37.9 18.6 10 Adelie Biscoe 40.5 18.9 # … with 158 more rows
Sorting rows
So far, we have looked at subsetting the data. But some times, we want to reorganize the data without altering it. In tables, we are used to be able to sort columns in ascending or descending order.
This can also be done with {dplyr}’s arrange() function. arrange does not alter the data per se, just the order in which the rows are stored.
penguins %>%
arrange(island)
# A tibble: 344 × 8
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 Adelie Biscoe 37.8 18.3 174 3400
2 Adelie Biscoe 37.7 18.7 180 3600
3 Adelie Biscoe 35.9 19.2 189 3800
4 Adelie Biscoe 38.2 18.1 185 3950
5 Adelie Biscoe 38.8 17.2 180 3800
6 Adelie Biscoe 35.3 18.9 187 3800
7 Adelie Biscoe 40.6 18.6 183 3550
8 Adelie Biscoe 40.5 17.9 187 3200
9 Adelie Biscoe 37.9 18.6 172 3150
10 Adelie Biscoe 40.5 18.9 180 3950
# … with 334 more rows, and 2 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>
Here we have sorted the data by the island column. Since island is a factor, it will order by the facor levels, which in this case has Biscoe island as the first category. If we sort a numeric column, it will sort by numeric value.
By default, arrange sorts in ascending order. If you want it sorted by descending order, wrap the column name in desc()
penguins %>%
arrange(desc(island))
# A tibble: 344 × 8
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 181 3750
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 186 3800
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 195 3250
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA NA
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 193 3450
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 190 3650
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 181 3625
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 195 4675
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 193 3475
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 190 4250
# … with 334 more rows, and 2 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>
Challenge 3
Arrange the penguins data set by
body_mass_g.Solution 3
penguins %>% arrange(body_mass_g)# A tibble: 344 × 8 species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_… body_mass_g <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> 1 Chinstrap Dream 46.9 16.6 192 2700 2 Adelie Biscoe 36.5 16.6 181 2850 3 Adelie Biscoe 36.4 17.1 184 2850 4 Adelie Biscoe 34.5 18.1 187 2900 5 Adelie Dream 33.1 16.1 178 2900 6 Adelie Torgersen 38.6 17 188 2900 7 Chinstrap Dream 43.2 16.6 187 2900 8 Adelie Biscoe 37.9 18.6 193 2925 9 Adelie Dream 37.5 18.9 179 2975 10 Adelie Dream 37 16.9 185 3000 # … with 334 more rows, and 2 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>
Challenge 4
Arrange the penguins data set by descending order of
flipper_length_mm.Solution 4
penguins %>% arrange(desc(flipper_length_mm))# A tibble: 344 × 8 species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> 1 Gentoo Biscoe 54.3 15.7 231 5650 2 Gentoo Biscoe 50 16.3 230 5700 3 Gentoo Biscoe 59.6 17 230 6050 4 Gentoo Biscoe 49.8 16.8 230 5700 5 Gentoo Biscoe 48.6 16 230 5800 6 Gentoo Biscoe 52.1 17 230 5550 7 Gentoo Biscoe 51.5 16.3 230 5500 8 Gentoo Biscoe 55.1 16 230 5850 9 Gentoo Biscoe 49.5 16.2 229 5800 10 Gentoo Biscoe 49.8 15.9 229 5950 # … with 334 more rows, and 2 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>
Challenge 5
You can arrange on multiple columns! Try arranging the penguins data set by ascending
islandand descendingflipper_length_mm, using a comma between the two arguments.Solution 5
penguins %>% arrange(island, desc(flipper_length_mm))# A tibble: 344 × 8 species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> 1 Gentoo Biscoe 54.3 15.7 231 5650 2 Gentoo Biscoe 50 16.3 230 5700 3 Gentoo Biscoe 59.6 17 230 6050 4 Gentoo Biscoe 49.8 16.8 230 5700 5 Gentoo Biscoe 48.6 16 230 5800 6 Gentoo Biscoe 52.1 17 230 5550 7 Gentoo Biscoe 51.5 16.3 230 5500 8 Gentoo Biscoe 55.1 16 230 5850 9 Gentoo Biscoe 49.5 16.2 229 5800 10 Gentoo Biscoe 49.8 15.9 229 5950 # … with 334 more rows, and 2 more variables: sex <fct>, year <int>
Putting it all together
Now that you have learned about ggplot, filter, select and arrange, we can have a look at how we can combine all these to get a better understanding and control over the data. By piping commands together, we can slowly build a better understanding of the data in our minds.
We can for instance explore the numeric columns arranged by Island
penguins %>%
arrange(island) %>%
select(where(is.numeric))
# A tibble: 344 × 5
bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g year
<dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <int>
1 37.8 18.3 174 3400 2007
2 37.7 18.7 180 3600 2007
3 35.9 19.2 189 3800 2007
4 38.2 18.1 185 3950 2007
5 38.8 17.2 180 3800 2007
6 35.3 18.9 187 3800 2007
7 40.6 18.6 183 3550 2007
8 40.5 17.9 187 3200 2007
9 37.9 18.6 172 3150 2007
10 40.5 18.9 180 3950 2007
# … with 334 more rows
And we can continue that by looking at the data for only male penguins
penguins %>%
arrange(island) %>%
select(island, where(is.numeric)) %>%
filter(sex == "male")
Error in `filter()`:
! Problem while computing `..1 = sex == "male"`.
Caused by error:
! object 'sex' not found
Whoops! What happened there? Try looking at the error message and see if you can understand it.
Its telling us that there is no sex column. How can that be?
Well, we tok it away in our select!
Since we’ve only kept numeric data and the island column, the sex column is missing!
The order in which you chain commands together matters. Since the pipe sends the output of the previous command into the next, we have two ways of being able to filter by sex:
- by adding sex to our selection
- by filtering the data before our selection.
Challenge 6
Fix the previous code bit by applying one of the two solutions suggested.
Solution 6
penguins %>% arrange(island) %>% select(sex, island, where(is.numeric)) %>% filter(sex == "male")# A tibble: 168 × 7 sex island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g year <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <int> 1 male Biscoe 37.7 18.7 180 3600 2007 2 male Biscoe 38.2 18.1 185 3950 2007 3 male Biscoe 38.8 17.2 180 3800 2007 4 male Biscoe 40.6 18.6 183 3550 2007 5 male Biscoe 40.5 18.9 180 3950 2007 6 male Biscoe 40.1 18.9 188 4300 2008 7 male Biscoe 42 19.5 200 4050 2008 8 male Biscoe 41.4 18.6 191 3700 2008 9 male Biscoe 40.6 18.8 193 3800 2008 10 male Biscoe 37.6 19.1 194 3750 2008 # … with 158 more rowspenguins %>% filter(sex == "male") %>% arrange(island) %>% select(island, where(is.numeric))# A tibble: 168 × 6 island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g year <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <int> 1 Biscoe 37.7 18.7 180 3600 2007 2 Biscoe 38.2 18.1 185 3950 2007 3 Biscoe 38.8 17.2 180 3800 2007 4 Biscoe 40.6 18.6 183 3550 2007 5 Biscoe 40.5 18.9 180 3950 2007 6 Biscoe 40.1 18.9 188 4300 2008 7 Biscoe 42 19.5 200 4050 2008 8 Biscoe 41.4 18.6 191 3700 2008 9 Biscoe 40.6 18.8 193 3800 2008 10 Biscoe 37.6 19.1 194 3750 2008 # … with 158 more rows
We can even combine such pipes with ggplot. Perhaps, in our case so far, the most convenient can be applying a filter before plotting data, which would reduce the data plotted to just the data we are interested in.
penguins %>%
filter(sex == "male") %>%
ggplot(aes(bill_length_mm)) +
geom_bar()
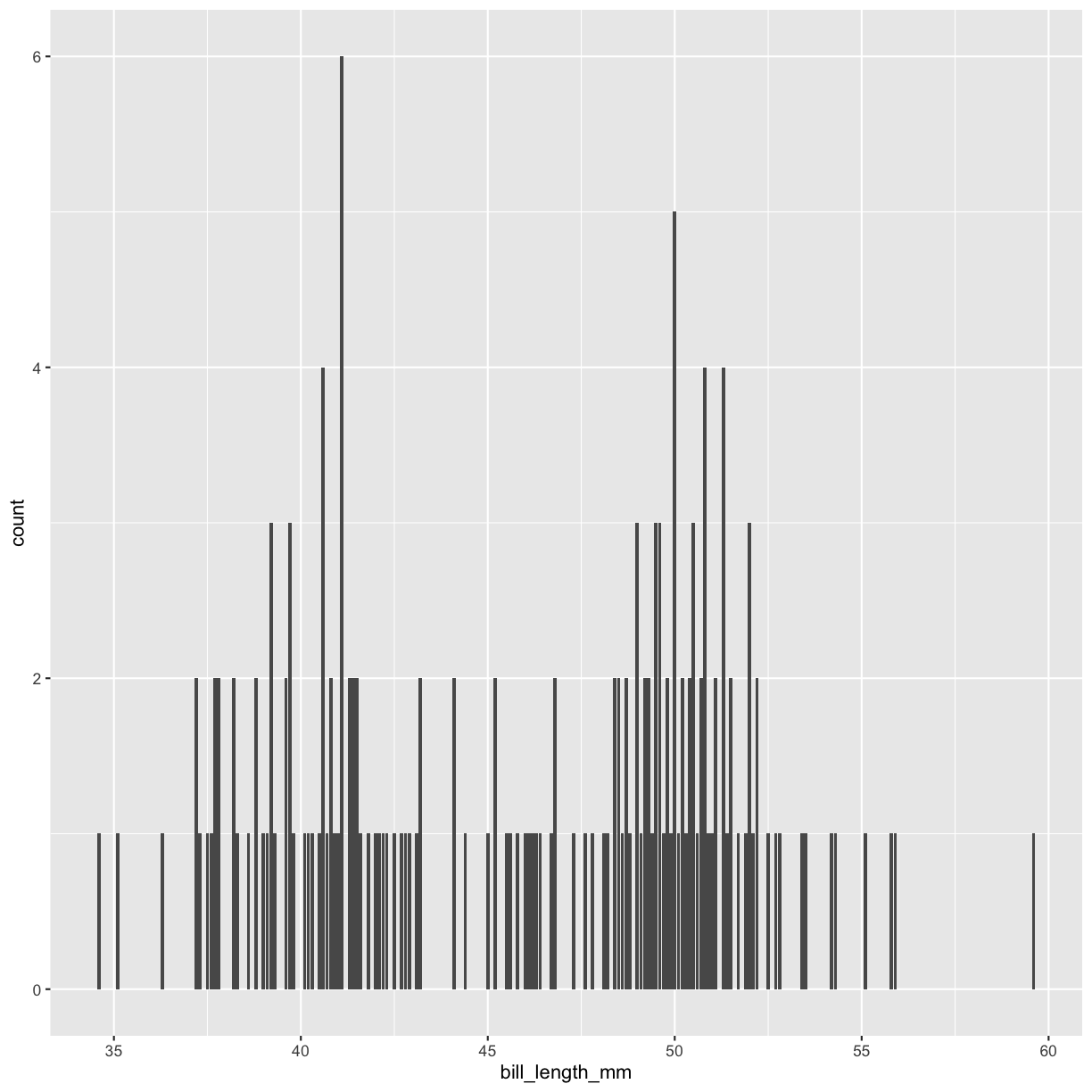
Now we only plot data from the male penguins, if we are particularly interested in those. This can be quite convenient if you have particularly large data and need to reduce it to get a proper idea of what the variables really look like.
Challenge 7
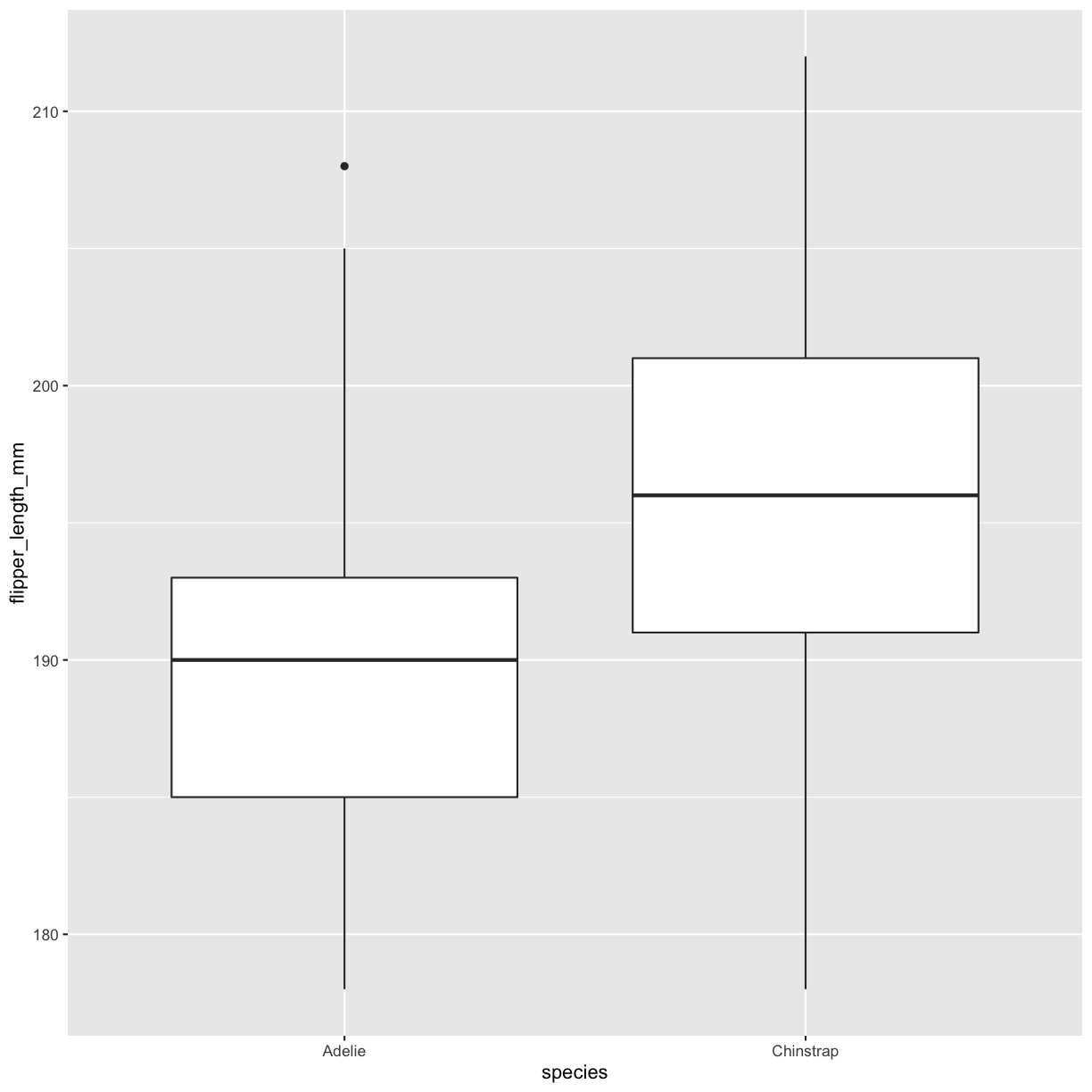
Create a plot of only data from the Dream island, putting flipper length on the y-axis and species on the x-axis. Make it a box-plot. Hint: Try geom_boxplot
Solution 7
penguins %>% filter(island == "Dream") %>% ggplot(aes(x = species, y = flipper_length_mm)) + geom_boxplot()
Wrap-up
Now we’ve learned about subsetting and sorting our data, so we can create data sets that are suited to our needs. We also learned about chaining commands, the use of the pipe to create a series of commands that build on each other to create a final wanted output.
Key Points
Using
arrangeUsing the pipe